📦 Understanding Package Managers on Ubuntu 📦
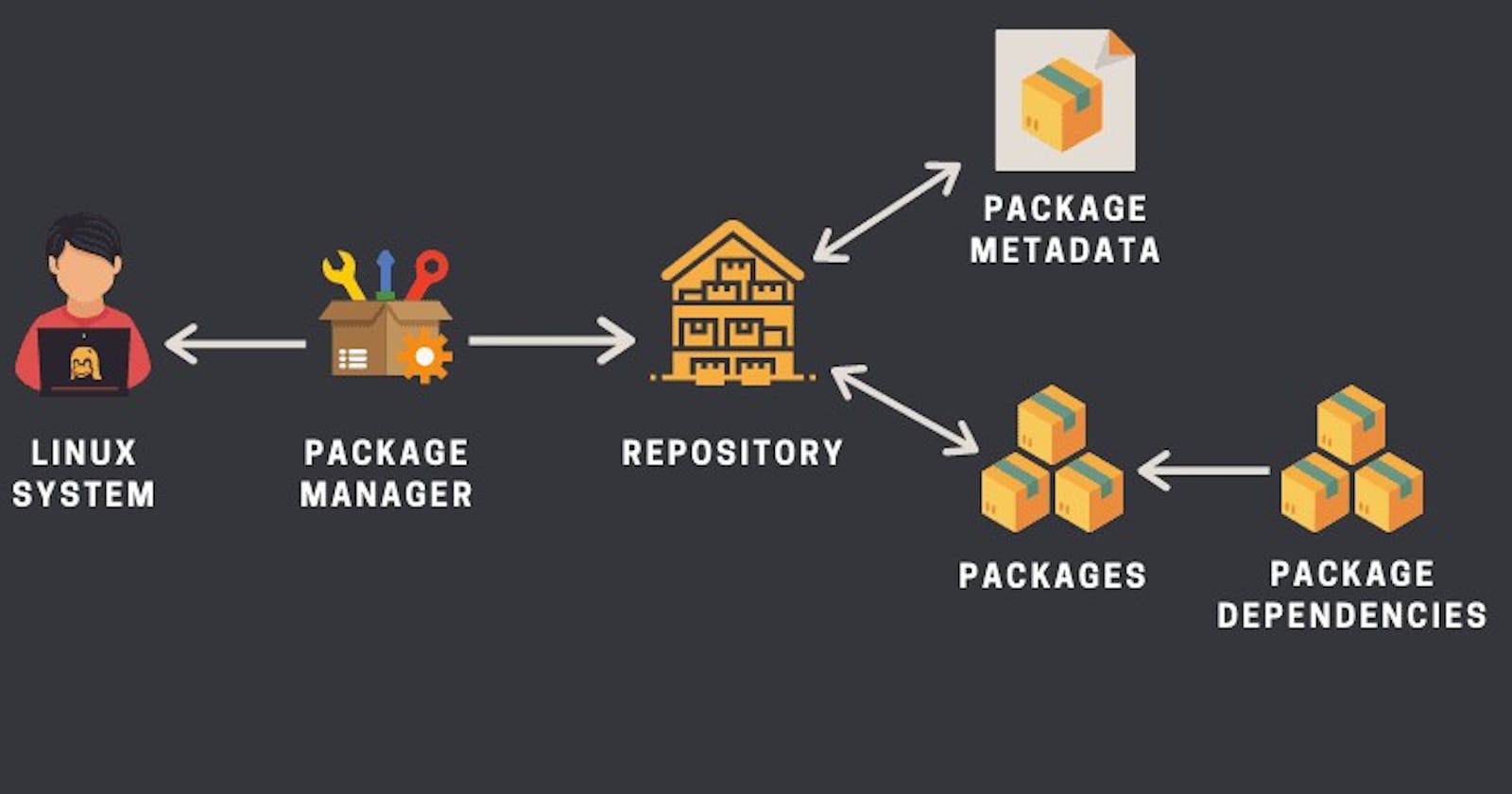
Package managers are like digital shopping assistants for your computer. They simplify the process of installing, updating, and managing software on your system. Think of them as app stores for your operating system, allowing you to easily find and install various programs and libraries. On Ubuntu, a popular Linux distribution, two commonly used package managers are APT (Advanced Package Tool) and DPKG.
APT: This is your primary tool for managing packages. It's responsible for fetching packages from online repositories and installing them with all their dependencies.
DPKG: This works at a lower level and is used to install individual Debian package files. APT actually uses DPKG in the background.
Now that we've got the basics, let's dive into how to use package managers to install two important tools: Docker and Jenkins.
🐳 Installing Docker on Ubuntu Using Package Managers 🐳
Docker allows you to put applications and their dependencies into containers for consistent and reliable deployment. Here's how to get started:
Open Your Terminal: Launch the terminal on your Ubuntu system.
Update Package List: Run the following command to ensure you have the latest package information:
sudo apt updateInstall Docker's Dependencies: You need a few things before you can install docker. Get them by running:
sudo apt install apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl software-properties-commonAdd Docker Repository: This adds the official docker repository to your system:
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.gpg echo "deb [arch=amd64 signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.gpg] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu $(lsb_release -cs) stable" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/nullInstall Docker Engine: Update your system and now install docker using apt package manager.
sudo apt update sudo apt install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.ioStart and Enable Docker: These commands ensure Docker starts on boot:
sudo systemctl start docker sudo systemctl enable dockerVerify Installation: Check if Docker is installed and running.
docker --version

🤖Setting Up Jenkins on Ubuntu Using Package Managers 🤖
Jenkins is an automation tool that makes building, testing, and deploying software easier. Let's get it up and running:
- Update/Install JDK on your system
sudo apt update
sudo apt install openjdk-17-jre
java -version
Update Package List: Update your package list to include the Jenkins repository:
sudo apt updateInstall Jenkins: Now install jenkins using APT package manager.
curl -fsSL https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable/jenkins.io-2023.key | sudo tee \ /usr/share/keyrings/jenkins-keyring.asc > /dev/null echo deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/jenkins-keyring.asc] \ https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable binary/ | sudo tee \ /etc/apt/sources.list.d/jenkins.list > /dev/null sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install jenkinsStart and Enable Jenkins: Start the jenkins service and set it to start on boot.
sudo systemctl start jenkins sudo systemctl enable jenkinsGet initial Admin Password: Retrieve the initial admin password to complete setup.
sudo cat /var/lib/jenkins/secrets/initialAdminPassword
🎉 Conclusion 🎉
Congratulations! You've just installed Docker and Jenkins on your Ubuntu system using package managers. 🎈 Package managers simplify software management, making it as easy as adding items to your online shopping cart. Docker containers and Jenkins automation are powerful tools that can greatly enhance your development workflow. Now you're equipped with the ability to seamlessly manage and deploy software. Remember, these tools are essential in the modern world of software development, and understanding how to use them will make your life much easier. Happy coding! 😄🚀